Nestin and Clic1 in cancer cells: Their mechanics and functions
We have elucidated the mechanism by which nestin, a type of intermediate filament, softens cancer cells by increasing mobility of cytoskeletal filament protein. Cancer cells expressing high levels of nestin can pass through narrow gaps during invasion, thus increasing their metastatic ability.

We established a nestin knockout cell by are genome editing.
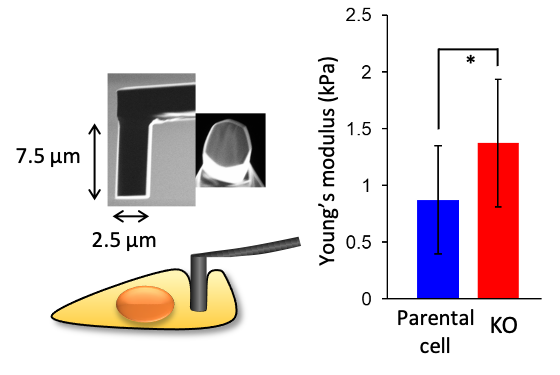
The elastic modulus of nestin knockout cells is higher than that of parental cell.
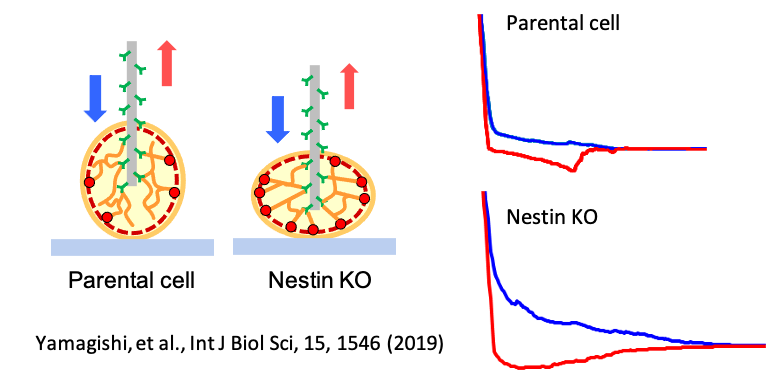
Mobility of intermediate filament vimentin was successfully analyzed in living cells with antibody-modified nanoneedles.
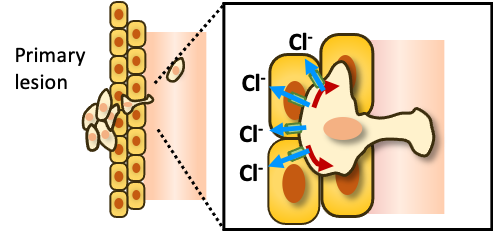
We are developing a method to evaluate the chloride ion efflux ability during cell compression.