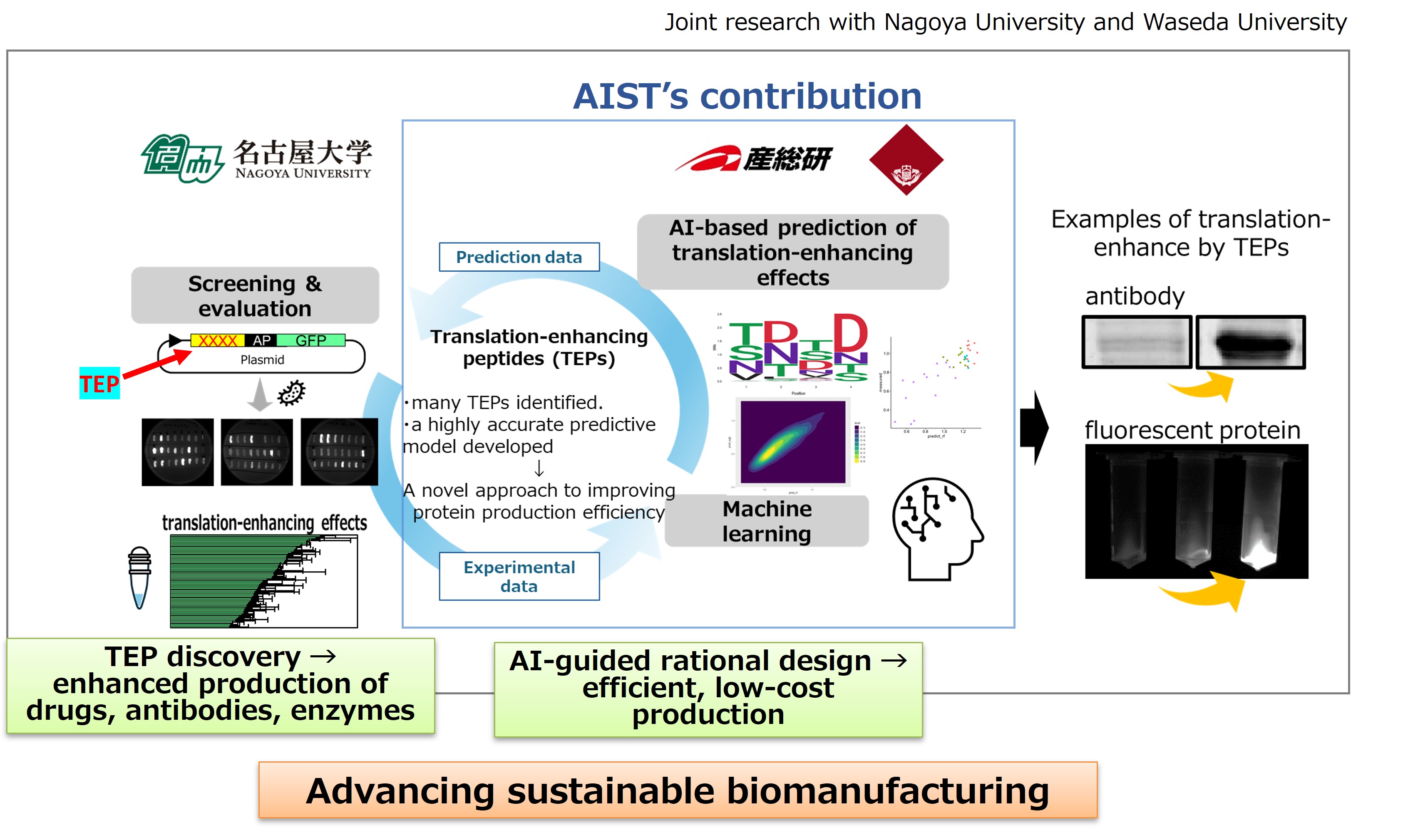
Development of a new technology for microbial protein production
Researchers from Nagoya University, AIST, and Waseda University have previously reported that certain short peptide sequences can enhance protein translation and reduce ribosome stalling. Based on this finding, they screened artificially randomized peptide libraries to identify peptides that suppress ribosome stalling, and discovered numerous new Translation-Enhancing Peptides (TEPs). Each TEP exhibited a different level of translation-enhancing activity, leading to improved protein production efficiency. Furthermore, the team developed an AI-based machine-learning model capable of predicting translation-enhancing activity directly from peptide sequences.
The model showed a high correlation with experimental data, demonstrating its potential as a rational design tool for selecting peptide sequences optimized for target proteins.
*For more details, please see the press release below.
A new approach to increasing protein production efficiency using short peptide sequences
Press Release
Publication
Title: Screening and machine learning‒based prediction of translation-enhancing peptides that reduce ribosomal stalling in Escherichia coli
Authors: Teruyo Ojima-Kato, Gentaro Yokoyama , Hideo Nakano , Michiaki Hamada and Chie Motono
Journal: RSC Chemical Biology
DOI: 10.1039/d5cb00199d