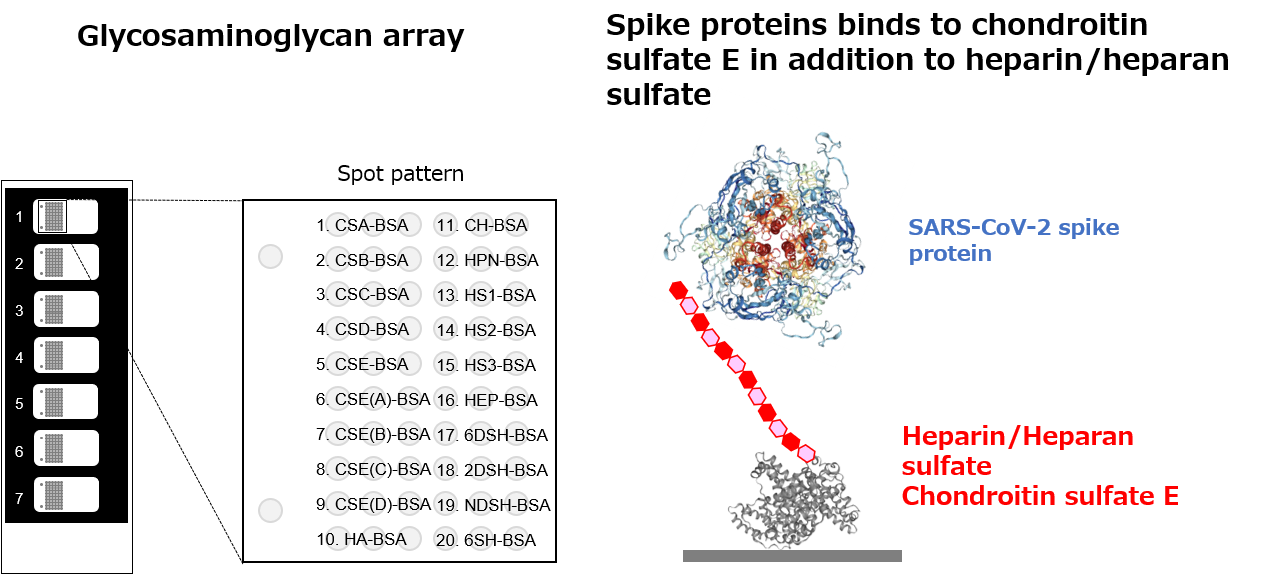
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binds to chondroitin sulfate E
Recently, it has been reported that heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan is an attachment factor that promotes infection with SARS-CoV-2. Here, we developed a glycosaminoglycan array in which 20 types of GAGs were arranged on a slide glass, and analyzed the glycan binding specificity of the spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2. The S protein bound to chondroitin sulfate E in addition to heparin/heparan sulfate. The S1 subunit, which interacts with the ACE2 receptor, selectively bound to heparin, while the S2 subunit strongly bound to chondroitin sulfate E in addition to heparin/heparan sulfate. In addition to heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate E has also been shown to have the potential to function as an attachment factor in infection with SARS-CoV-2.
This research is the result of joint research with Seikagaku Corporation.
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binds to chondroitin sulfate E
Collaboration
- Seikagaku Corporation
Publication
- Title: A glycosaminoglycan microarray identifies the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to chondroitin sulfate E
- Authors: Tomoko Watanabe, Ko Takeda, Keiko Hiemori, Toshikazu Minamisawa, Hiroaki Tateno
- Journal: FEBS Lett. 2021 Aug 10.
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14173.