The paper by Kuno, Sakaue, and colleagues has been selected as a "Paper in Forefront" in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.
A recent research article entitled “Analytical Dissection of Minor Glycoforms and Glycoprotein Associations in rAAV Preparations by Multimodal Glycoproteomics”, authored by Atsushi Kuno (Group Leader), Hiroaki Sakaue (Researcher), and colleagues in collaboration with Professor Susumu Uchiyama of Osaka University, has been selected as a Paper in Forefront in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, a leading analytical chemistry journal published by Springer Nature.
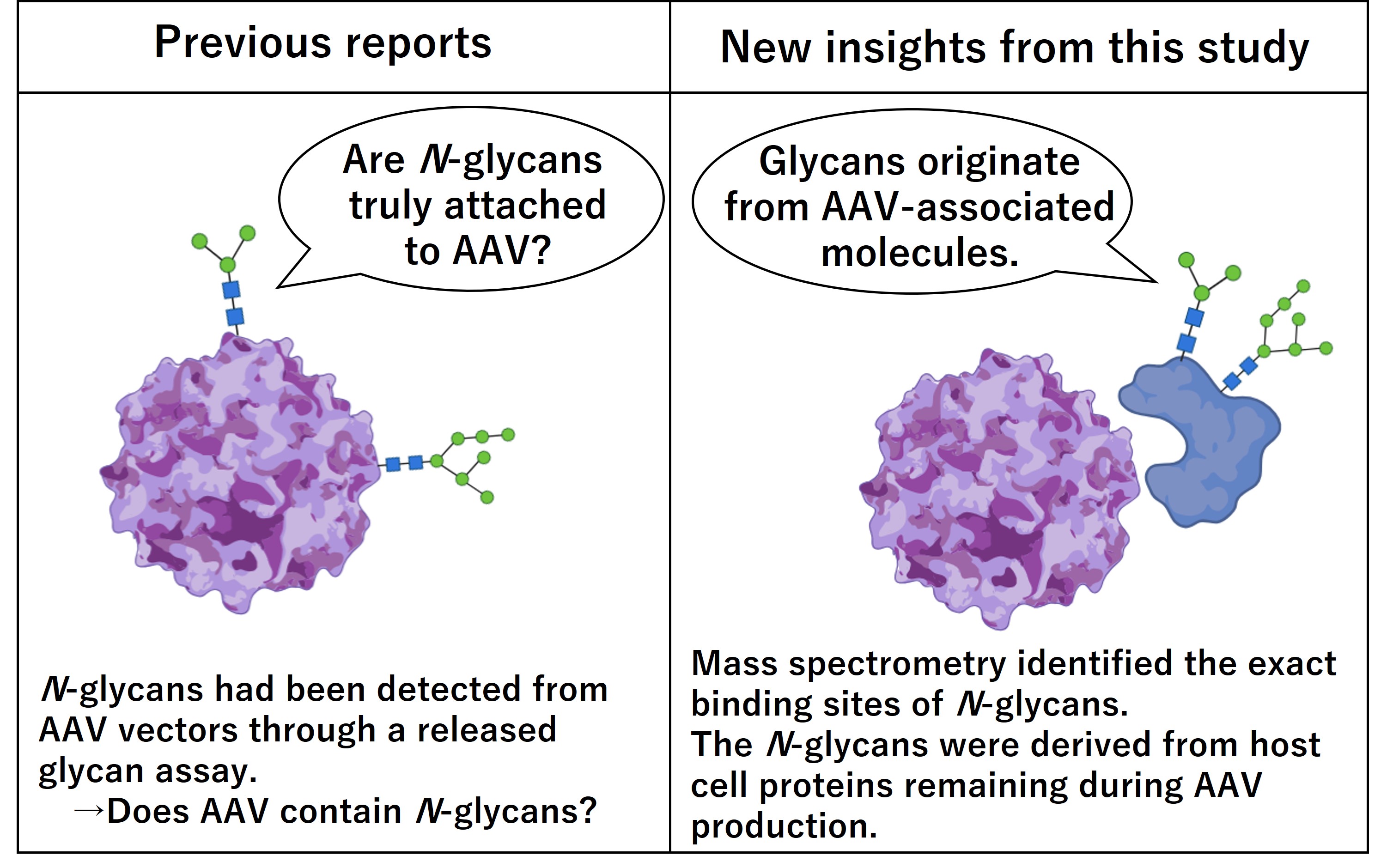
This study focused on the detailed glycan analysis of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, which are widely used in gene therapy. Previous reports presented conflicting evidence on whether AAV particles are directly modified with N-glycans. By combining lectin-based enrichment with advanced glycoproteomic mass spectrometry, the research team revealed that although less than 1% of AAV particles were captured by lectins, N-glycans were not present on the AAV itself. Instead, the N-glycans were found to originate from trace amounts of host cell proteins that interact with AAV.
These findings offer important insights for the quality control and manufacturing optimization of AAV-based therapeutics and are expected to contribute to improving the reliability of future gene therapy technologies.
Collaboration
Osaka Univ
Publication
Title: Analytical Dissection of Minor Glycoforms and Glycoprotein Associations in rAAV Preparations by Multimodal Glycoproteomics
Authors: Atsushi Kuno, Hiroaki Sakaue, Sachiko Koizumi, Azusa Tomioka, Saho Mizukado, Yuki Yamaguchi, Mitsuko Fukuhara, Yasuo Tsunaka, Hiroyuki Kaji, Susumu Uchiyama
Journal: Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a grant-in-aid from the 'Research and development of core technologies for gene and cell therapy' supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) [grant number JP23ae0201001 and JP23ae0201002]