Research Groups
Task-Intelligent Robotics RG | Field Robotics RG | Trustworthy Robotics RG |
Smart Mobility RG | CNRS-AIST JRL (Joint Robotics Laboratory), IRL3218 |
Mitsubishi Electric-AIST Human-Centric System Design CRL
Task-Intelligent Robotics Research Group
| Research site: | AIST Tokyo Waterfront | |
|---|---|---|
| HP: | https://unit.aist.go.jp/icps/icps-am/ | |
| member | ||
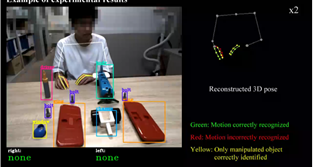
Article handling technology by robots
- Picking unknown parts without teaching
- Using AI and simulator it is possible to pick complex parts (e.g. tangled)
- Applicable to parts supply in factories and automation of store's display work.
- Determine which object and how it is being manipulated using images
- Applicable for the analysis of expert workers, robot motion planning, etc.
 |
 |
||
| Picking unknown parts assuming factory suply parts | Motion recognition of human, transfer to robot |
Field Robotics Research Group
| Research site: | AIST Tsukuba Central 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| HP: | https://unit.aist.go.jp/icps/icps-fr/ | |
| member | ||
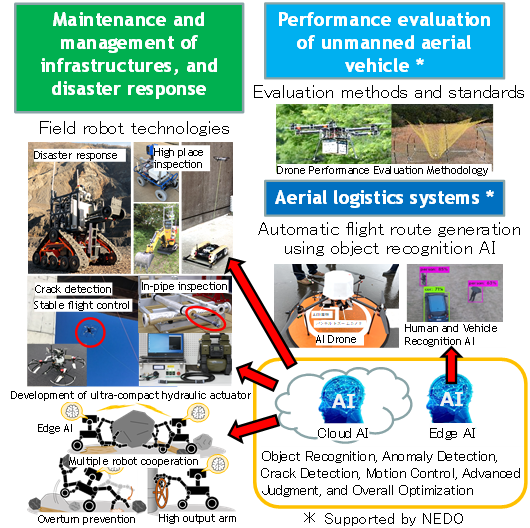
R & D of field robotics for maintenance and management of social/industrial infrastructure, and disaster response, including:
- Access technologies using land-sea-air field robots
- Ultra-compact hydraulic actuators to improve workability and motion performance of field robots
- Intelligent field robot technologies using Edge AI and Cloud AI
- Aircraft technical standards and control technical standards
 |
Trustworthy Robotics Research Group
| Research site: | AIST Tsukuba Central 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| HP: | - | |
| member | ||
R&D, standardization for safety of service robots, industrial robots, and their testing methods
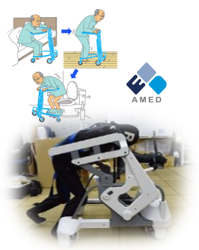
- Safety and effectiveness standards and testing methods for nursing care robots (AMED Project to Promote the Development and Introduction of Robotic Devices for Nursing Care)
- Risk assessment, safety certification schemes for agricultural robots, logistics robots, and station service robots
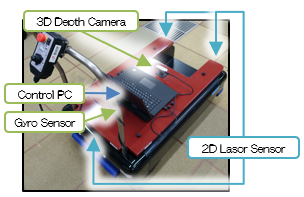
- Evaluation and testing technologies for optical safety sensors, a flexible robot-exterior sensor, and human detection sensors
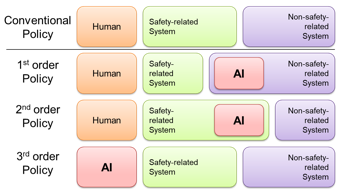
- AI quality and reliability standards to ensure robot safety
- Safety evaluation platform for AI-equipped robots
 |
 |
||
| Toileting action aids | Testing for safety sensors | ||
 |
 |
||
| AI-equipped robots DRC-3 | AI Safety 3 Policies |
Smart Mobility Research Group
| Research site: | AIST Tsukuba Central 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| HP: | - | |
| member | ||
The Smart Mobility Research Team is developing intelligent technologies
for personal mobility that coexist with pedestrians and operate in shared
spaces, in order to ensure short-distance transportation means for the
elderly and others with limited mobility. In addition to software development
for safe and comfortable driving support and autonomous driving, the team
conducts fundamental research on mobility robots, including map generation,
self-localization, environmental perception, and path planning, utilizing
sensing technologies and machine learning.
SLAM/Mapping and Localization
- Novel method for high-precision, real-time LiDAR mapping
- 3D interactive SLAM system that improves mapping accuracy with minimal user input
- LiTAMIN: LiDAR SLAM with improved accuracy using ICP with covariance regularization
- VITAMIN-E: A new monocular SLAM system using high-density feature points and fast optimization
- 4D Attention: A gaze-based mapping technique for dynamic scenes
- C*: Robust monocular visual localization using prebuilt 3D maps
- A new method and dataset for pedestrian detection in walking spaces
- SeqSLAM++ for robust self-localization and navigation in outdoor environments
CNRS-AIST JRL (Joint Robotics Laboratory), IRL3218
| Research site: | AIST Tsukuba Headquarters and Information Technology Collaborative Research Center | |
|---|---|---|
| HP: | https://unit.aist.go.jp/isri/isri-jrl/en/ | |
| member | ||
The CNRS-AIST Joint Robotics Laboratory (JRL) is an international collaborative
research organization established by the National Institute of Advanced
Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) of Japan and the French National
Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS). Using humanoid robots as the main
research platform, Japanese and French researchers work together to advance
autonomy in robotics. Key research areas include task and motion planning,
control, perception, human-environment interaction, and cognitive robotics.
Within this internationally diverse environment, the lab actively engages
in many international collaborative projects, including those funded by
the European Union. JRL is officially recognized as an International Research
Laboratory (IRL) by both AIST and CNRS.
Behavior Generation and Autonomy Based on Intelligence and Learning
- Ant’noid: A memory-efficient spatial navigation method for humanoid robots
- Development of a robot foundation model for real-world robotic behavior based on a multimodal AI foundation model
- InteractivePlanning: A planning method that enhances task adaptability through human-assisted instruction for robot autonomy
- RLOptMCP: Whole-body motion generation for humanoids through contactability prediction and optimization
- Z: Enhancing robot exploration via large-scale learning models for 3D learning, high-level object recognition, and visual servoing
- CALL: A robot control method for dynamic object handover, integrating human biomechanics and visual perception
- HICAN: Development of an advanced control framework that combines the precision of industrial robots with the safety of collaborative robots
- iCPH: A unified framework for humanoid motion understanding through continual learning, prediction, and generation of contact motions
- ImpAdm: Design of a nonsmooth force control strategy for admittance-type robots operating under overload and impact conditions
- Friends: Collaborative research on humanoid robots for aircraft manufacturing
Mitsubishi Electric-AIST Human-Centric System Design Cooperative Research Laboratory
| Research site: | AIST Tokyo Waterfront | |
|---|---|---|
| HP: | - | |
| member | ||
As a countermeasure for the declining working-age population due to the
falling birthrate and aging population, all industrial sectors, including
manufacturing, are required to improve the Quality of Working (QoW) and
labor productivity of their employees. In addition, remote work is becoming
more prevalent, and the comfort of working spaces such as home or satellite
offices is also attracting attention.
Here, by focusing on the QoW of individuals, it is necessary to create an environment to maximize their abilities according to their working style and physical condition. In building the environment, it is important to establish a system that allows for control of the working environment without the constraints of physical and geographical space, as well as a system that allows for multiple tasks according to the capabilities of the individual.
This collaborative laboratory aims to realize integrated solutions that improve productivity and deliver a high level of comfort through a comfortable working environment with high QoW.
Here, by focusing on the QoW of individuals, it is necessary to create an environment to maximize their abilities according to their working style and physical condition. In building the environment, it is important to establish a system that allows for control of the working environment without the constraints of physical and geographical space, as well as a system that allows for multiple tasks according to the capabilities of the individual.
This collaborative laboratory aims to realize integrated solutions that improve productivity and deliver a high level of comfort through a comfortable working environment with high QoW.
 |