The cloud coverage data are used to select the images for image
matching in the SWIR parallax correction and the inter-telescope
registration, since cloud-free images are essential for image
matching. The algorithm is based on the fact that clouds have the
highest reflectivity in the visible and the short wave infrared
spectral region except for snow and ice, and a low emission in the
thermal infrared spectral region because of their lower temperature
than targets on the earth.
It will be very important to distinguish clouds from snow and ice
on the earth's surface. The discrimination is carried out using
knowledge that snow/ice may be brighter in band 2 and darker in band
4 than cloud.
The EOSAT algorithm is employed for cloud coverage calculation.
Figure 2-11 (a) shows the algorithm flow. The bands 2, 4 and 11 data
are used as representative data for the visible, short wave and
thermal infrared spectral regions, respectively. Two threshold
values of T2 and T2* , two threshold values of T4 and T4* and one
threshold value of T11 are introduced for band 2, band 4 and band 11,
respectively, as the borders between cloudy and cloud-free targets.
According to this algorithm the hatched regions shown in Figure
2-11(b) are judged to be cloudy.
The calculation is carried out for every block whose size is 20 x
20 SWIR pixels. The threshold value depends on the latitude and the
season.
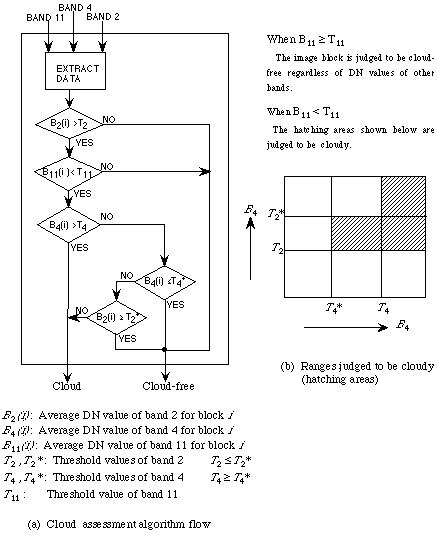
Figure 2-11 Cloud assessment algorithm
|