
Research
CO2 as a Fuel Resource!?
Synthesis of Gaseous Fuels Using "High-Temperature Electrolysis": e-methane
The emission of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the use of fossil fuels such as petroleum and coal has a significant impact on global warming. Furthermore, from the perspective of future depletion of fossil resources, the development of technologies that can reuse CO2 as a fuel resource would enable a stable supply of new resources for future generations.
One method proposed to ensure a stable supply of new resources for the future is fuel synthesis technology, such as methane synthesis, using "high-temperature electrolysis" developed by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST). With this high-temperature electrolysis technology, it is possible to simultaneously electrolyze H2O and CO2 to synthesize a synthesis gas consisting of hydrogen (H2) and carbon monoxide (CO). This synthesis gas is known as a raw material gas for various fuels, and it is possible to efficiently convert it into gaseous fuels such as methane (e-methane) continuously. By manufacturing gaseous fuels such as synthetic methane from H2O and CO2, existing gas supply facilities can be utilized. In other words, no additional investment in new facilities is necessary, simply by replacing conventional fossil fuels with synthetic methane.
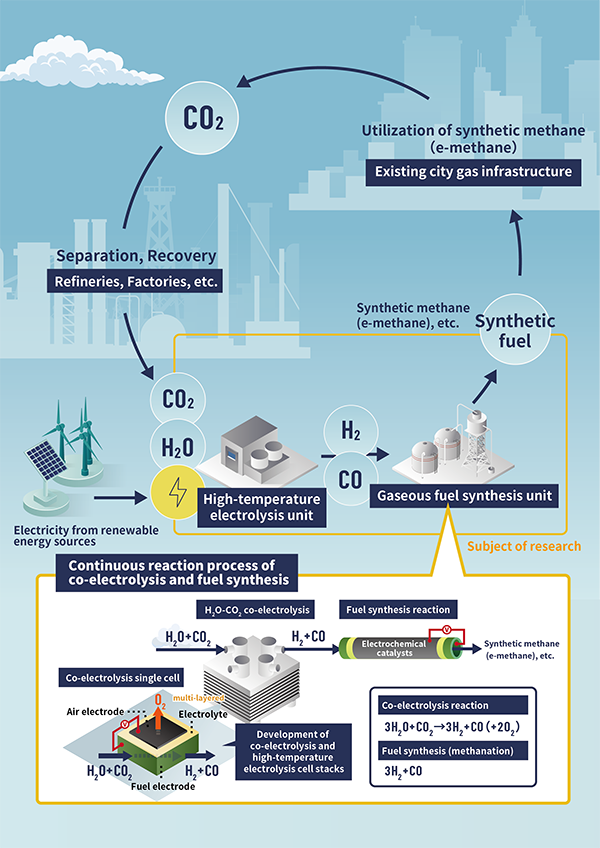
The idea of utilizing CO2 in this way originated more than a decade ago. The concept was introduced during a lecture on fuel cells in the United States, where it was discussed how interesting it would be if chemical substances could be created from CO2 and utilized as a resource energy. At that time, when fuel cell development was garnering attention worldwide, research was initiated to conduct reverse reactions (electrolysis) on self-developed fuel cells. Subsequently, with the support of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) CREST program (from FY2013 to FY2018) and the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) Leading Research program (from FY2019 to FY2020), fundamental technologies were developed leading to the joint adoption of the NEDO Green Innovation Fund project " Development of Technology for Producing Fuel Using CO2, etc. / Development of innovative technology for the production of synthetic methane / SOEC Methanation Technology Innovation Project" with Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. as the lead company. Under this project, AIST is responsible for research on fundamental technology of SOEC cell stacks and catalyst reaction control, and conducting research towards societal implementation by 2040.
